What is ultrasonic cleaning?
Ultrasonic cleaning, in simple terms, is a common technique for high-quality cleaning, that produces ultrasonic waves in fluid and creates microscopic implosions to remove the contamination. Typically, this method is used when the contamination is tightly adhered to solid surfaces of the parts, blinds holes, etc. Ultrasonic sound waves are transmitted in the fluid with a frequency of greater than 25 kHz to create ultrasonic effect. The components used in the US system and their configuration plays important role in effective cleaning.
This article covers the basic functions of the key components used in the ultrasonic cleaning system.
Components for Ultrasonic Cleaning
The basic components of an ultrasonic cleaning machine are:
- Generator
- Transducers
- Resonator
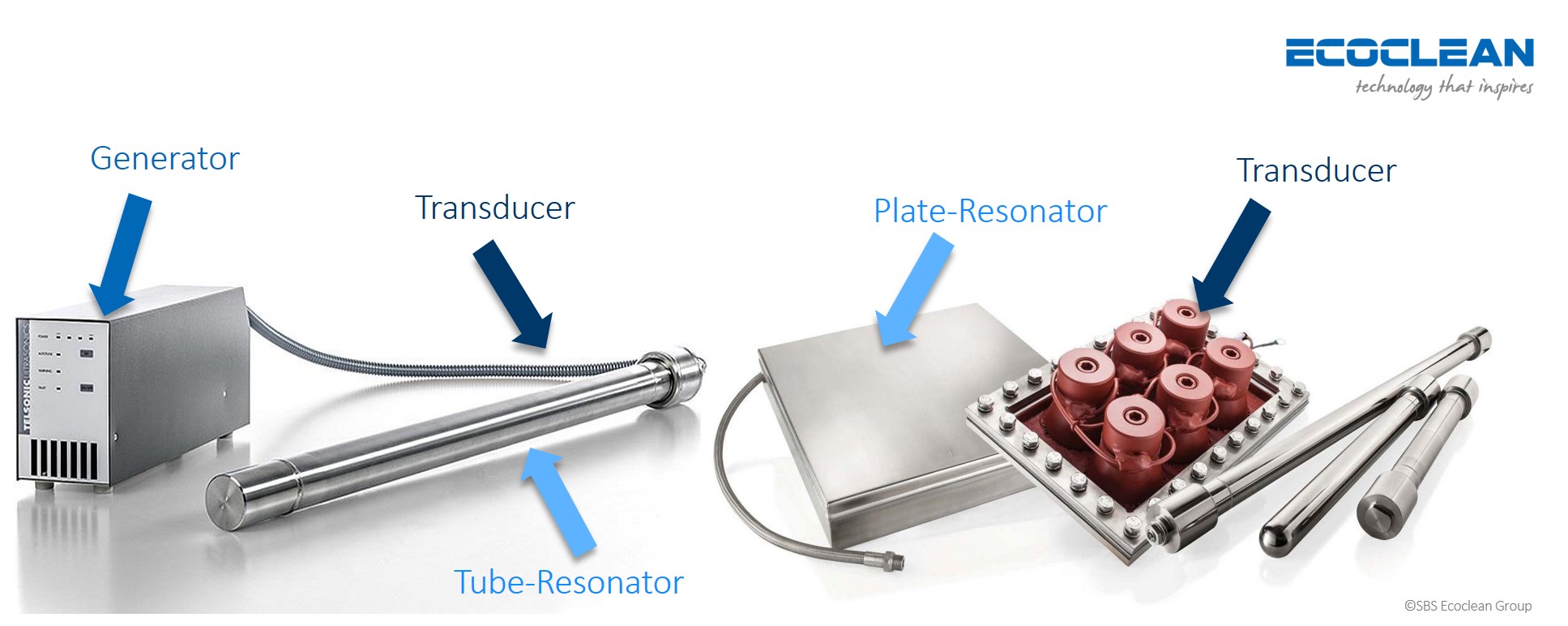
The ultrasonic cleaning machine is equipped with the components consists of generators, transducers and resonators. Basically, using these components, the US system generates high frequencies that cause the formation of microscopic cavitation bubbles in cleaning media. These bubbles then cause implosion and carry away the particles tightly adhered to the surface of the part.
- Generator:
The Generator is the head of the ultrasonic cleaning machine and it produces the high-frequency signals from the electric energy which is then supplied to transducers to convert to ultrasound waves. In addition to generating the signal, it can produce a range of frequencies and can control it to match specific cleaning requirement.
Normally, the power line provides electricity at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz depending on the country. The Generator converts the mains frequency into high-frequency ranging from 25 kHz, 40 kHz or even higher up to 1000 kHz to operate the transducer. This device is located outside the system and acts as part of an integrated or independent solution and generates the frequency at which the transducer operates.
- Transducer:
The Transducer is a device used to convert electromagnetic waves into mechanical vibrations of the same frequency. Transducers for the generation of ultrasound most commonly use piezoelectric materials to convert an electrical signal into mechanical motion.
The transducers need to be protected from heat and fluid. And hence are mounted in water-proof cabins or outside the cleaning chambers. These vibrations are then transferred to resonators which ultimately help in the cleaning action.
- Resonator:
The Resonator is a device that moves at the same frequency as the transducer and creates waves with high and low-pressure areas in the fluid.
Resonators are always coupled with transducers and form the heart of the Ultrasonic system. Resonators are submerged and mounted inside the cleaning chamber.
There are 2 basic types of designs of resonators
- Tube-Resonator:
- Efficiency: 90% – 97%
- Frequency: Available up to 40 kHz
- Vacuum Proof: Yes
- Application: All single chamber machines including aqueous and solvent-based cleaning systems
- Plate-Resonator:
- Efficiency: 60%
- Frequency: More than 40 kHz
- Vacuum Proof: Yes, possible
- Application: Ultrasonic bath and Multi-tank cleaning machines
Considering ever-evolving cleanliness requirements, Tube type resonators are recommended due to their higher capacity (Watts) even with a single resonator, high efficiency in transmitting the waves into mechanical vibrations and 360o coverage due to their design. Moreover, these are vacuum proof and works even with solvent-based cleaning systems.
Ultrasonic in the cleaning industry is one of the complex yet effective technique to enhance the cleaning process. To summarize, the components such as generator, transducer and resonator installed together forms a vital unit in US cleaning machine.
In our next blogs, we will see the physics of ultrasonic cleaning and see how cavitation helps to perform cleaning action. Watch this space for more updates. Visit www.ecoclean-india.com/blogs






